Palm Oil Dry Fractionation Introduction
Palm oil fractionation refers to the process of controlling the cooling and crystallization process of palm oil and separating it into low solubility liquid phase (soft fat) and high solubility solid phase (hard fat). Palm oil fractionation can divide palm oil into three components: hard fat, soft fat, and the middle part.
Hard fat mainly consists of S3 β- POP β- PPO triglycerides, the middle part mainly consists of β- POP, soft fats mainly consist of SU2 and U3 triglycerides. The solubility point of palm oil extracted from hard fat is generally around 50 ℃, while that of soft fat is generally around 24 ℃. Hard fat is suitable for manufacturing margarine and shortening, without causing slow crystallization, greasy sensation, and post hardening phenomenon, and greatly improving the plasticity range of fats. For example, when 70% stearin and 30% rapeseed oil are combined, the oxidation stability is good. Before ester exchange, it is a good bread oil, and after ester exchange, it is a good frying oil. Soft fat is an excellent frying oil. The melting point range in the middle part is narrow and close to human body temperature, which can be used as a substitute for cocoa butter.
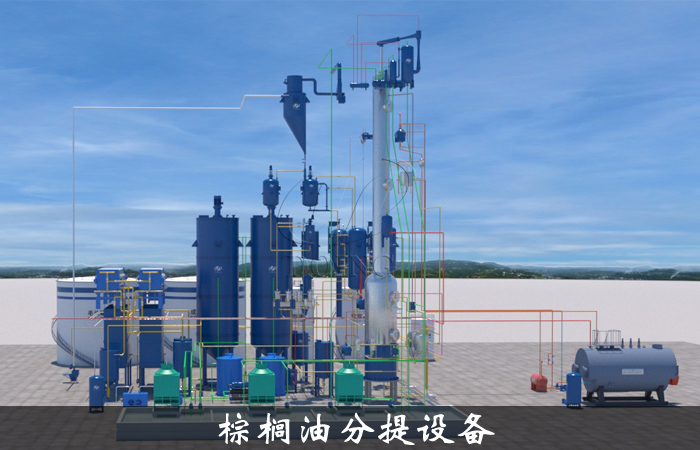

There are three commonly used methods for palm oil fractionation: dry fractionation, solvent extraction, and surfactant extraction.
The application of palm oil fractionation methods mainly depends on certain physical and chemical properties of the required soft and hard fats, with emphasis on the properties of hard fats. By changing the method and conditions of palm oil fractionation, different physical and chemical properties of stearin can be obtained. At the same time, soft fats with a small range of physical and chemical property changes can also be obtained.
Among the three extraction methods of dry extraction, solvent extraction, and surfactant extraction, the dry extraction process has the widest application prospect.
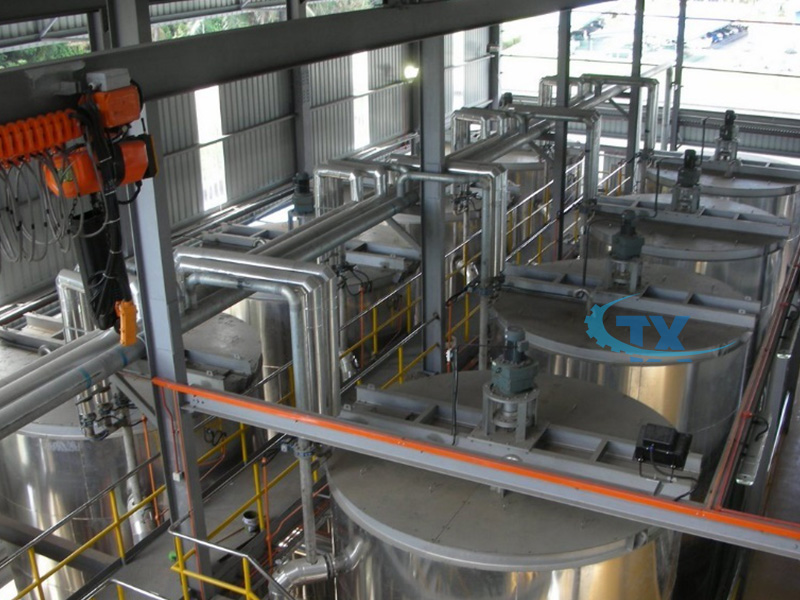

Palm oil Dry fractionation Introduction
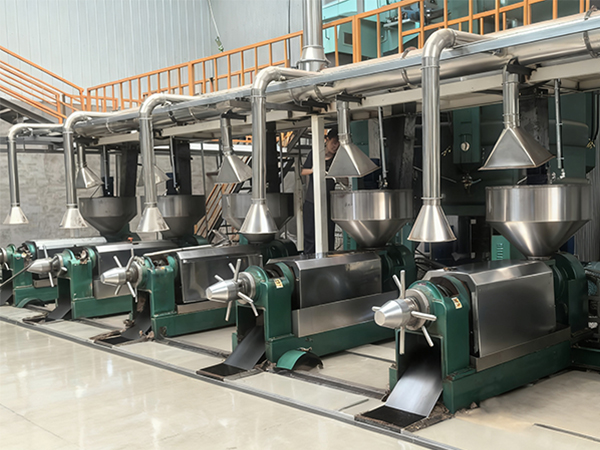
Dry fractionationn is the most economical method, which refers to slowly cooling the dissolved oil to a certain degree without adding any solvents, then filtering, separating, and crystallizing to precipitate solid esters.
Dry fractionation steps:
1. Heating
Palm oil is in a semi-solid state at room temperature, with saturated and unsaturated acids accounting for about 50% each. The composition of triglycerides is GS3 accounting for 8% to 10%, GS2U accounting for about 48%, GSU2 accounting for 35% to 39%, and GU3 accounting for 7% to 7.5%, respectively. The unique composition of palm oil determines its unique crystallization process. Palm oil is dissolved into a liquid state by steam heating before processing. Before crystallization, palm oil is generally further heated to around 70 ℃ to destroy all existing crystals.
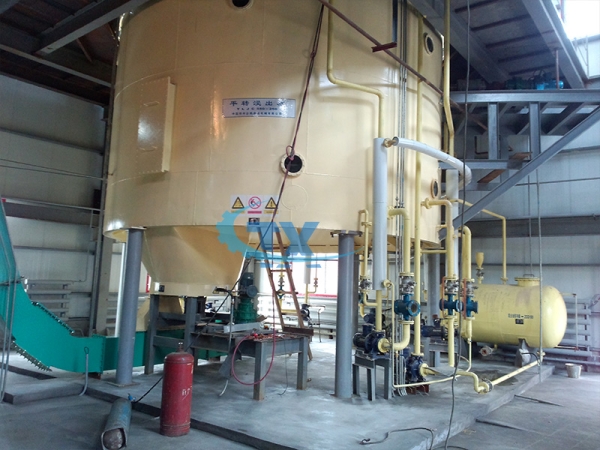
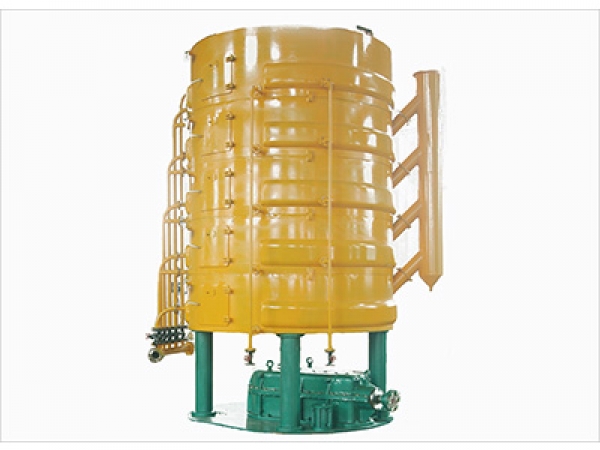
2. Cooling crystallization
The key to the dry fractionation process is cooling crystallization. If crystallization is successful, separation is easy. Therefore, the design of crystallizers is particularly important, as different types of crystallizers should have their own cooling exchange surfaces, cooling systems, and stirring structure characteristics. During the processing, the cooling crystallization conditions will determine the beginning of atomic nucleus crystallization, the number of crystals, and the size of crystals. Cooling efficiency and orderliness are decisive factors in ensuring the unique formation and filterability of crystal structures. Only in this way can stable, uniform, and filterable crystals be produced. The specific operation is to control the cooling process by setting the temperature difference and cooling time between the oil and cooling water while stirring and circulating water cooling, forming crystal nuclei and gradually growing. When the required temperature is reached (depending on the desired quality of the soft grease, usually 20 ℃), stop cooling.
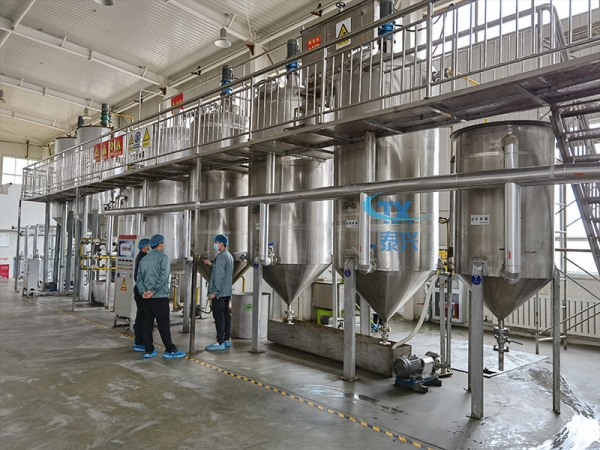
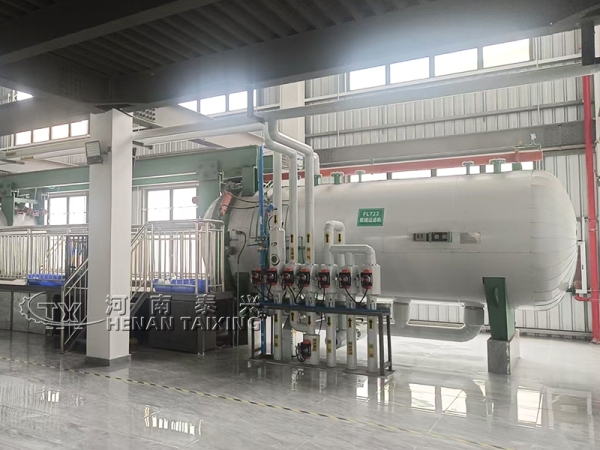
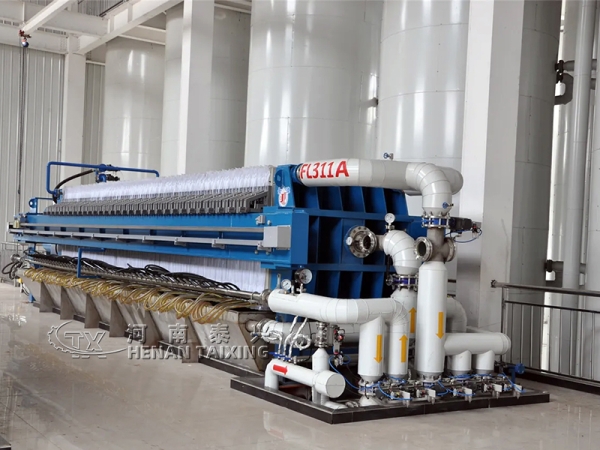
3. Filtering
The conditions for controlling cooling crystallization are certainly important, and the selection of filtration equipment also has a great impact on the yield of liquid oil.
There are currently several types of filtration systems used in industry: drum filter, continuous belt vacuum filter, and membrane filter. In the past decade or so, membrane filters have been widely used. Because compared with continuous belt vacuum filters and drum filters, membrane filters have a higher yield of soft grease (70% to 75%) and a higher hardness of hard grease, while the yield of soft grease separated by the other two filters is generally only 65%.
Advantages of Palm Oil Dry Fractionation
Dry fractionation has the advantages of simple process, high degree of automation control, low steam consumption, good product quality, no need for centrifugal separators, no need for any solvents, and no wastewater generation.